PrISM Respiratory |
||||||||||||||
 |
||
A
B
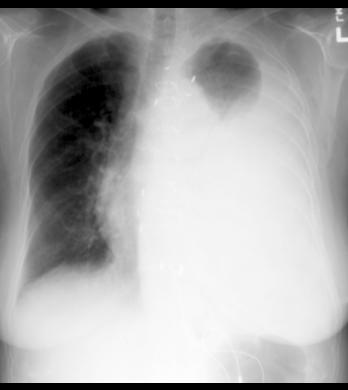
This patient has a very large left pleural effusion. The fluid makes a sharp interface with the small amount of remaining aerated left lung, and produces a curved outer margin (called a meniscus) like fluid in a glass does due to surface tension.
The heart and mediastinum are shifted slightly to the patient's right, consistent with a space-occupying lesion (fluid) on the left. If the left side were too white due to collapse, the heart and mediastinum would be pulled to the left instead of pushed to the right.
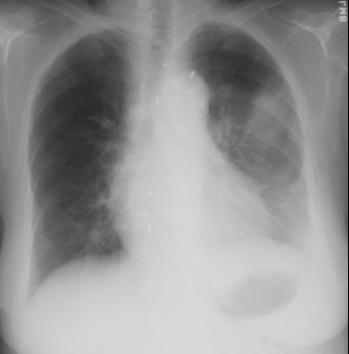
This is the chest radiograph done right after the pleural effusion was drained (2 liters), at which time the patient's shortness of breath was a bit worse. What do you think of the left lung?